In a world where millions of people are displaced by war, persecution, and violence, refugee visas serve as a lifeline for individuals seeking safety and stability. These visas offer refugees a legal pathway to resettle in another country that can grant them protection from the dangers they face in their home country. However, the journey to securing a refugee visa is not easy. The process can come with many challenges, not to mention the complex and legal bureaucratic processes.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how refugee visas work, explore the countries that offer them, and cover everything you need to know about this type of visa. At Checklist Visa, our goal is to educate you on various visa options and help make your immigration journey as smooth as possible.
What is a Refugee?
Under international law, a refugee is someone who is outside their home country and cannot or will not return due to a well-founded fear of persecution. This persecution must be based on one or more of the following grounds: race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group.
The 1951 Refugee Convention sets the standards for who qualifies as a refugee. It also grants legal protection and rights to those who meet this definition. To claim refugee status, a person must prove they face serious threats to their life or freedom in their home country. Returning home must pose a genuine risk to their safety.
How Do Refugee Visas Work?
The refugee visas serve as legal pathways for individuals fleeing persecution to move to another country where they can be safe. To obtain a refugee visa, an individual must first meet the criteria of a refugee under international law. He or she must demonstrate a well-founded fear of persecution based on race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or social group.
The process of applying for a visa can vary depending on the country. However, in general, individuals can apply from abroad (offshore) or from within the country where they are seeking asylum (onshore).
For those applying offshore, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) plays a crucial role. The UNHCR identifies refugees in need of protection and resettlement. To do this, they conduct interviews, verify claims, and assess eligibility for resettlement.
Once the UNHCR recognizes someone as a refugee, they refer them to a country with resettlement options. The host country then reviews the case and processes the refugee visa. During this process, they consider important factors such as security, health, and family reunification.
The process for applying for a refugee visa is often lengthy. It requires significant documentation to prove persecution, but it ultimately offers refugees a chance to rebuild their lives in a safe environment.
The Role of Refugee Visas
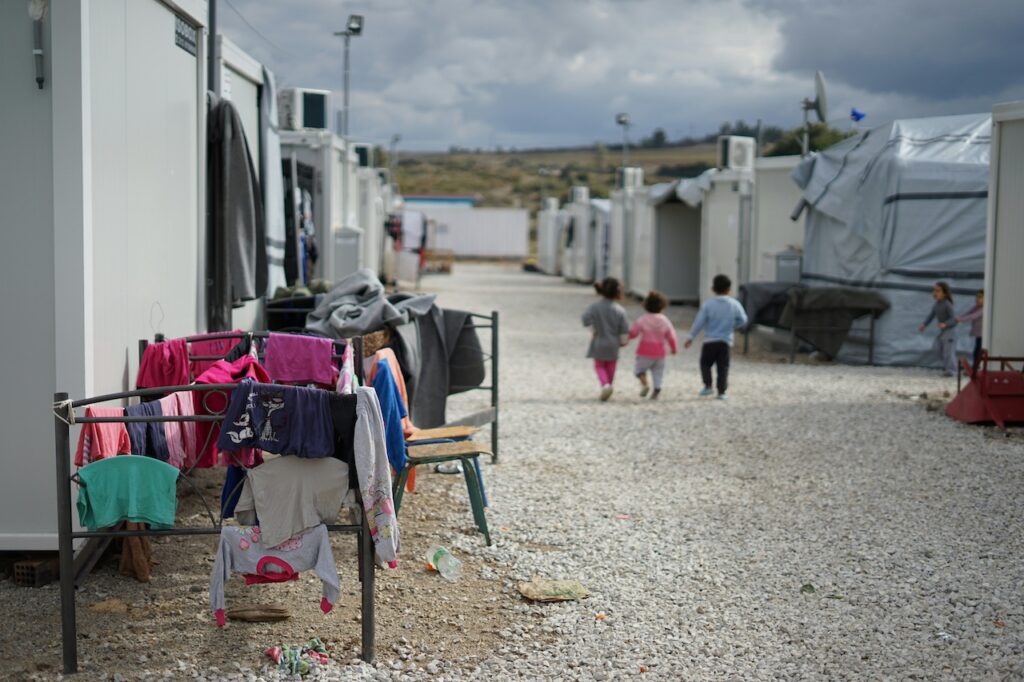

Refugee visas play a crucial role in providing a legal and safe escape route for individuals fleeing war-torn or dangerous nations. These visas are designed to offer temporary or permanent protection to people who face immediate threats to their safety due to war, persecution, or natural disasters.
Special visa categories also exist for specific populations in crisis. Examples are women at risk, unaccompanied minors, or those facing persecution due to their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Individuals requiring immediate evacuation from situations that threaten their lives can be issued emergency rescue visas. These visas provide them with a rapid pathway to safety in another country. Aside from saving lives, these visas also uphold international humanitarian obligations. It’s a means for some countries to contribute to the global efforts of protecting those who don’t feel safe in their home countries.
Countries Offering Refugee Visa Programs
Several countries are known for offering robust refugee visa programs and helping refugees resettle as part of their humanitarian commitments. Some of the most prominent include:
1. Canada
Canada is recognized worldwide for its comprehensive refugee resettlement programs. These include the Government-Assisted Refugees (GAR) Program and the Private Sponsorship of Refugees Program. Under these programs, private citizens can sponsor refugees. Canada consistently ranks as one of the top countries for refugee intake.
2. United States
The United States has a longstanding Refugee Admissions Program. They work closely with the UNHCR to resettle refugees. The country sets an annual refugee admissions cap and resettles individuals fleeing persecution worldwide.
3. Germany
As part of the European Union, Germany is a leading country in refugee protection. The country is particularly known for providing refugee visas to asylum seekers and refugees from war-torn regions like Syria. Germany has also implemented various integration programs to help refugees resettle and adapt to their new communities.
4. Sweden
Sweden is best known for its progressive policies on refugee protection and resettlement. The European country provides refugees with access to housing, healthcare, and education.
5. Australia
Under the Humanitarian Program of Australia, the country issues offshore refugee visas, offering protection to individuals in refugee camps or living outside their home country due to persecution.
FAQs on Refugee Visas

How long does the refugee visa process take?
The refugee visa process can take a long time. It often depends on several factors. First, the applicant must be screened for eligibility. Then, security and medical checks are required. These steps can take several months. In some cases, it may take years, especially if there is a backlog of cases. The process also depends on the country’s visa policies and the urgency of the refugee’s situation. Applicants should be prepared for a lengthy wait when applying for a refugee visa.
Can refugee visa holders bring their family members?
Yes, refugee visa holders may bring their family members. This is called family reunification. Usually, close family like spouses and children can join them on their resettlement to the new country. However, this will usually depend on the country’s rules. Refugees must apply for their family to come after their visa is approved. Some countries may allow parents or other relatives in special cases. Family members will need to go through security and health checks too. The goal is to keep families together and help them start a new life in safety.
What happens if my refugee visa application is denied?
If your refugee visa application is denied, you have options to consider. First, check the reason for the denial. Sometimes, missing documents or errors cause the rejection. You might be able to fix the issue and reapply. In other cases, you can appeal the decision if the country allows it. This means you ask for your case to be reviewed again. It’s important to understand the specific appeal process for that country. If appealing is not possible, you may explore other visa or protection options.